Lactobacillus amylovorus SGL14
The study conducted in our laboratories, in association with the Zooprophylactic Institute of Teramo, consisted of feeding two groups of mouse models:
the first group was given a diet rich in oxalates; the second
group was offered the same diet introducing the mix
Phyllantin 14® . In the study, several parameters were evaluated in addition to the levels
of oxalates, including creatinine and blood glucose levels. The evidence
scientific studies have demonstrated a decrease in oxalate levels in the group of mice taking Phyllantin 14® . Furthermore, after three weeks of treatment, the intestinal microbiota of the animals treated with Phyllantin 14® showed intestinal colonization deriving from L.amylovorus SGL14.

Meccanismo d'azione
L. amylovorus SGL14 utilizes metabolically produced oxalates and
those derived from the diet, as a source to colonize the host's gastrointestinal tract. This results in a decrease in available oxalate
for absorption and therefore a reduction in the amount excreted through the urine.
In this way, SGL14 has demonstrated its ability to modulate the levels of endogenous oxalates and those taken in through food. ¹
L. amylovorus SGL14 has been patented as a microorganism having antimicrobial activity.
1. L Manna, E Rizzi, E Bafile, C Macchi, M Ruscica, R Salini, E.Rossi, C.Panebianco, V Pazienza, F.Federici, (2020), Impact of Phyllantus niruri and Lactobacillus amylovorus SGL 14 in a mouse model of dietary hyperoxaluria


Scientific Studies
Phyllanthus niruri
Phyllanthus niruri contains several categories of phytoconstituents including flavonoids, tannins, coumarins and saponins and has hepatoprotective properties and anti-inflammatory activity . The extract helps maintain urinary tract functionality and modulate carbohydrate levels .
Experimentally, in our laboratories, the association of P. niruri with the probiotic SGL14 was found to be effective in the different phases of stone formation and aggregation , also promoting the antispasmodic activity of smooth muscles and facilitating the elimination of urinary stones with a significant reduction in stone growth .
STUDIES: Phyllanthus niruri has been used to treat related disorders
to the urogenital organs, hypothesizing that the extract helps to improve renal disease in diabetes mellitus. The aim of the study was to investigate the effects of P. niruri on renal functions. The extract was administered orally to diabetic male rats for 28 days. The results showed
shown that the administration of P. niruri helps to maintain stable the
June blood glucose levels, creatinine clearance (CCr), blood uric nitrogen (BUN), BUN/CCr ratio, serum electrolytes, uric acid and proteinuria levels. The expression of inflammatory, fibrotic and apoptotic markers in the kidney was reduced, while the expression of proliferative markers increased after treatment.
Conclusion: P. niruri helps to preserve renal function and prevent histopathological changes by improving oxidative stress, inflammation, fibrosis and apoptosis and at the same time kidney health in cases of type II diabetes mellitus. ²
2. Nelli Giribabu, Kamarulzaman Karim, Eswar Kumar Kilari, Naguib Salleh, J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Jun 9:205:123-137 – Phyllanthus niruri leaves aqueous extract improves kidney functions, ameliorates kidney oxidative stress, inflammation, fibrosis and apoptosis and enhances kidney cell proliferation in adult male rats with diabetes mellitus
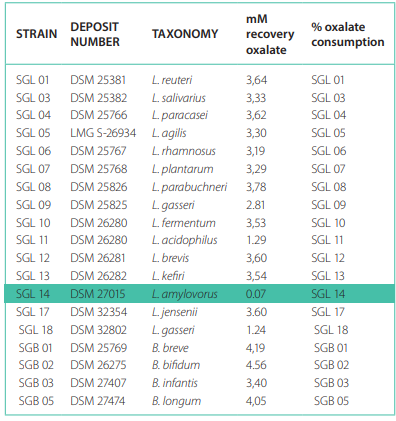
Screening result of oxalate degradation activity among different lactobacilus strains
The oxalate degradation activity was tested on different strains of the genus Lactobacillus. Among these, L. amylovorus SGL14 was found to be the most effective strain.